Corporate Social Entrepreneurship (CSE) differs from Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as the former comprises of a broader process, or organisational journey, by which the latter is part. Moreover, CSE is not just another form of CSR, but rather a process to strengthen and promote its development. CSE aims to provide an approach that will accelerate the CSR journey.
The following figure represents the journey of an organisation from CSR to CSE.
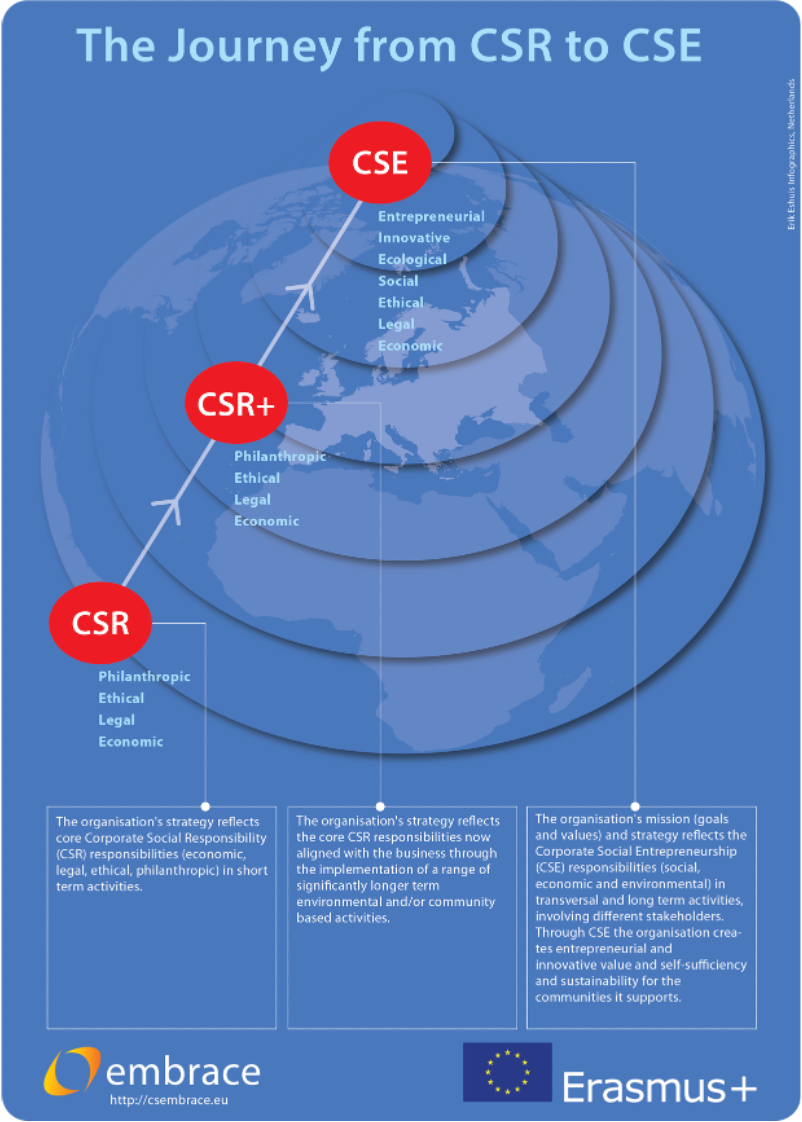
(EMBRACE project, 2021)
Stage 1 CSR
CSR occurs when companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and in their interaction with their stakeholders on a voluntary basis. It opens a way of managing change and of reconciling social development with improved competitiveness” (European Commission, 2001: 7).
Main components of CSR:
Stage 2 CSR+
Main components of CSR+:
When at this stage, the organisation’s strategy reflects the core CSR responsibilities now aligned with the business through the implementation of a range of significantly longer term environmental and/or community based activities.
Stage 3 CSE
Main components of CSE:
CSE promotes creation of shared value. This shared value is aligned with the triple bottom perspective, which refers to the total value equation that should be considered by organisations and which comprises notonly the financial or economic value, but also the environmental and social dimensions oforganisational performance (Elkington, 2008).